How Much Did It Cost To Repair The Tri State Tornado
Aeriform Damage Photos | Ground Damage Photos | Xenia F5 Track Map
The Apr iii-4, 1974 Super Outbreak affected xiii states across the eastern United states of america, from the Great Lakes region all the way to the Deep South. In all, 148 tornadoes were documented from this consequence, of which 95 were rated F2 or stronger on the Fujita scale and 30 were F4 or F5. Aside from all the castastrophic damage they left backside, the tornadoes resulted in
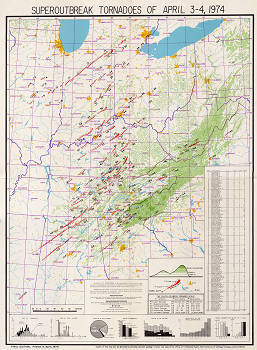
Detailed Super Outbreak tornado path and intensity analysis, hand drawn by Dr. T. Theodore Fujita of Academy of Chicago. (click for high-res version)
Some of the strongest tornadoes from this outbreak occurred right hither in the Ohio Valley. Dozens of tornadoes struck Ohio, Indiana, and Kentucky, resulting in 159 deaths, over 4000 injuries, and hundreds of millions of dollars in property damage. 2 vehement F5 tornadoes destroyed much of Xenia and Sayler Park (a western suburb of Cincinnati) in Ohio. Resulting in 34 deaths, the Xenia tornado was the deadliest of all tornadoes from this outbreak and remains amid the top ten costliest U.S. tornadoes on record (approximately $250 million in 1974). Several other strong F2 to F4 tornadoes also touched down during the Super Outbreak across southeast Indiana, northern Kentucky, and southwest Ohio, an surface area that today encompasses NWS Wilmington, Ohio's alarm surface area.
National Conditions Service office boundaries and technology were quite dissimilar back in 1974. The Atmospheric condition Service Function (WSO) in Cincinnati served the greater Cincinnati Tri-Country area while WSO Dayton was responsible for the Miami Valley and west-primal Ohio. In those days, non every NWS role was equipped with a radar. A WSR-57 (Atmospheric condition Surveillance Radar - 1957) was installed at WSO Cincinnati in 1960, giving NWS meteorologists coarse reflectivity data but no velocity data, which fabricated it extremely difficult to discover tornadoes. Storms on the radar screen were traced onto thin paper maps, and meteorologists heavily relied on the manifestation of hook echoes likewise as spotter reports when issuing tornado warnings. WSO Dayton did non have a radar of its own but utilized a facsimile automobile tied into Cincinnati'due south WSR-57 (also known by its identifier, CVG) display.
When the CVG radar displayed hook echoes and other impressive storm features outside WSO Cincinnati's warning area on Apr 3, meteorologists there made calls to the appropriate neighboring offices. At one point, the CVG radar screen displayed five distinct hook echoes--more than than
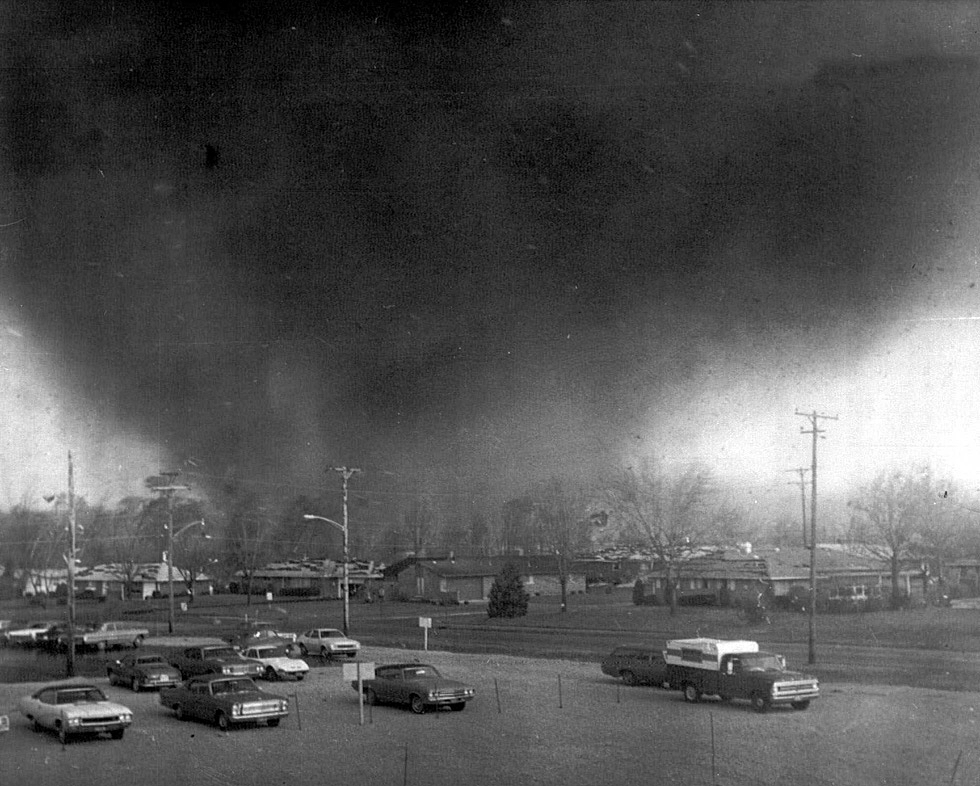

A massive F5 tornado bears down on Xenia. Photograph taken from the Greene Memorial Hospital by Fred Stewart.
Nigh an hour after the Xenia tornado, another tearing F5 tornado took aim at the western suburbs of Cincinnati. The merely tri-state twister of the Super Outbreak, this tornado originated well-nigh Rising Sun in Indiana around 5:xxx PM, passed through Kentucky, and then crossed the Ohio River

A view of the Sayler Park tornado as information technology moved through the Bridgetown area. Photo taken by Frank Altenau.
In the aftermath of this horrific event, many lessons were learned that have since been applied by various government agencies to mitigate hazards in subsequent severe weather outbreaks. Improvements in communications, warning systems, emergency preparedness, and forecast techniques and equipment take been implemented since the Super Outbreak, with the end consequence existence increased lead times for warnings, more accurate forecasts of events, greater public sensation, and more reliable communications.
 The Cincinnati Post |  The Cincinnati Post |  The Kentucky Mail |  The Cincinnati Mail |
 Letter of the alphabet from Dr. T. Fujita to | 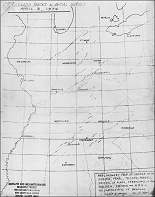 Preliminary Super Outbreak |  Super Outbreak tornado |  Fujita's Super Outbreak |
 Weather observer'southward brush | 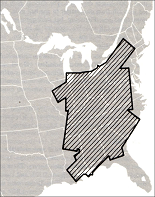 Total area covered by | 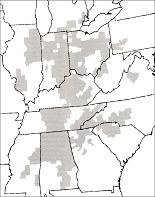 April 3-4, 1974 tornado | 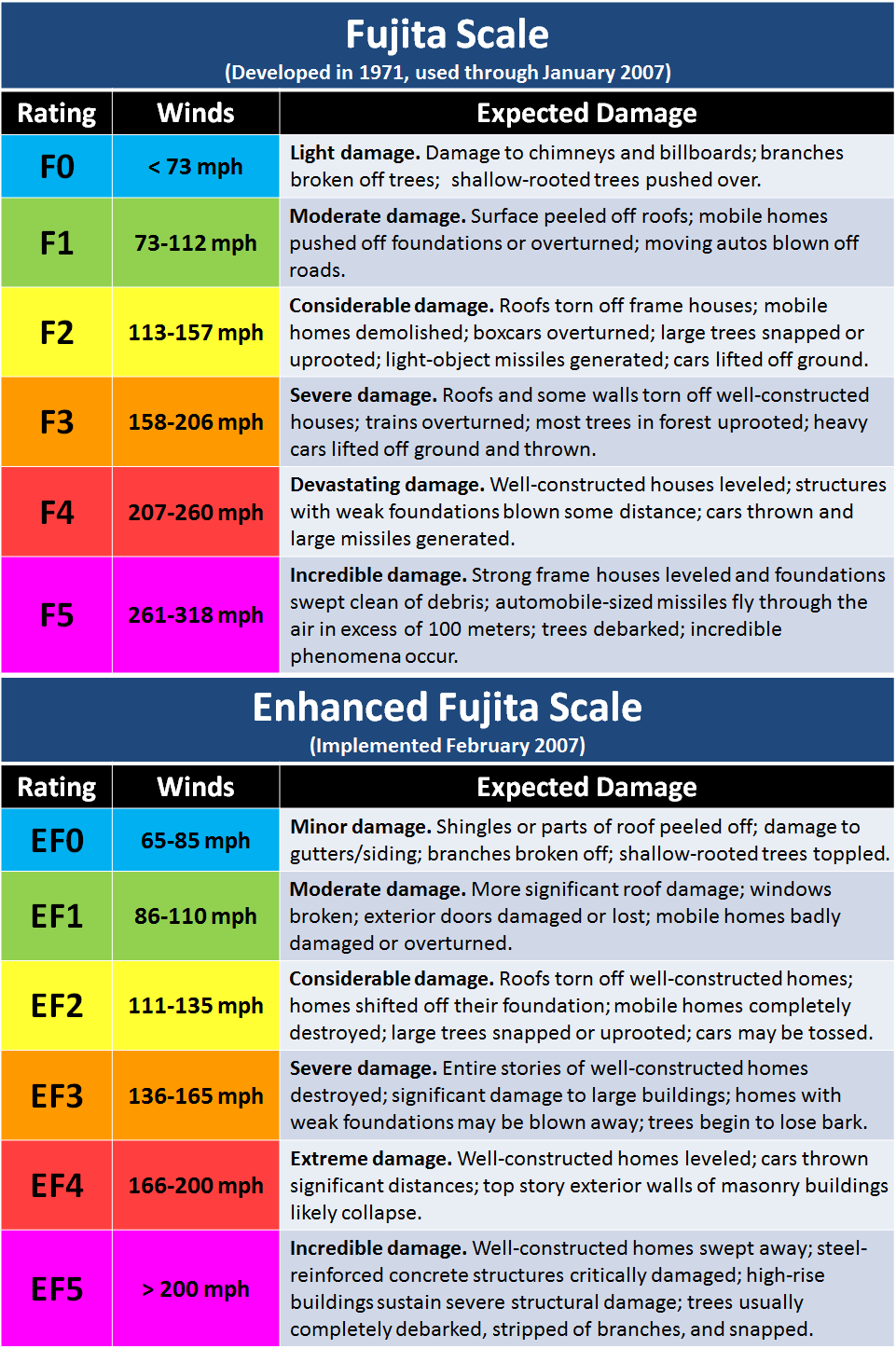 Comparison of Fujita Scale |
 Courtesy of the Ohio Historical Society, from their Ohio Memory collection. |  Plaque honoring those | ||
A 1978 documentary of the Super Outbreak, showing bodily footage of tornadoes as they
struck Xenia, Cincinnati, and Louisville, causing massive damage and numerous deaths.
Includes discussion of accelerate tornado preparation and emergency coordination.
Courtesy of the National Archives.
How Much Did It Cost To Repair The Tri State Tornado,
Source: https://www.weather.gov/iln/19740403
Posted by: perazarettest.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How Much Did It Cost To Repair The Tri State Tornado"
Post a Comment